Diseases of the veins and large blood vessels are accompanied by significant changes in their physical condition, which negatively affects the quality of the circulatory process. Varicose veins, which can significantly reduce a patient's quality of life due to poor digestion and blood flow to the body, require a careful attitude and timely initiation of treatment. This pathology may be accompanied by secondary lesions of the digestive system or may occur and continue on its own.
However, in any case, dilated esophageal veins and subsequent varicose veins are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms that allow the lesion to be identified in the early stages of development and the therapeutic effect to be started in time to prevent complications. Medical statistics note that this pathology of esophageal veins occurs predominantly in the male population (women are twice as likely to be affected by esophageal varicose veins as men), whereas the average age at which the first manifestations of the disease are 50-55 years is observed.
Causes of the disease
The causes of esophageal varices may vary depending on the onset of the disease and the general condition of the patient's body, and the set of causes may vary. However, varicose veins in the veins of the digestive system are in any case the result of changes in the general condition of the veins. The occurrence of varicose veins with such localization is due to the excessive hypertension of the venous circulation, which is most common in cirrhosis of the liver.
And such an extension can result in massive bleeding, the danger of which lies in the absence of symptoms, which is a warning: bleeding from the esophageal varices is often profuse, posing a real threat to the general condition of the esophagus. patient. Therefore, knowledge of the manifestation of this pathology of the esophageal veins and the measures taken to prevent the disease allow the disease to be diagnosed as soon as possible and the appropriate therapeutic effect to begin.
In addition, the following conditions may cause abnormalities in the veins of the digestive tract:
- congestion observed in the portal vein;
- portal thrombosis;
- development of malignant goiter;
- esophageal angioma.
The occurrence of this lesion may also be caused by the symptoms and vascular pathologies associated with Randu-Osler disease. All of these diseases and conditions are accompanied by negative changes in the circulatory system and digestive system, which initially affects the general condition of the veins and large arteries of the esophagus and gastric tissue. Changes in the circulatory system of internal organs such as the liver, spleen, gallbladder can cause varicose lesions of the esophagus.
Patient symptoms
The main manifestations of conditions such as varicose veins in the esophagus are bleeding. This symptom is observed in the absence of warning manifestations, in the background of so-called "complete health. "Signs of impending bleeding are mild throat tickling and a characteristic blood taste (salty-sour) when swallowed. The blood formed during bleeding during varicose veins usually resembles a vivid scarlet fever, which can resemble coffee grounds. Such frequent and profuse bleeding results in dizziness, weakness, and loss of consciousness.

As the causes of varicose veins can be exacerbated by various changes in the internal organs and the circulatory system as a whole, the overall quality of the function of these organs is largely determined by both the likelihood of and the accompanying varicose veins.
A symptom of an abnormality in the digestive system is bleeding, which develops during the asymptomatic course of the initial manifestations of the disease. Such bleeding can be insignificant, which does not immediately attract the patient's attention, or is abundant, with a high risk of death. The varicose veins seen in the tissues of the esophagus and stomach are most often characterized by a lack of significant changes that allow for timely recognition and treatment. However, this disease is one of the most frightening: with sudden bleeding characterized by abundant blood release, there is a high probability of the patient dying. According to medical statistics, four out of five cases of manifestation and exacerbation of gastrointestinal varicose veins occur in the patient.
Types and extent of esophageal varicose veins
Today, experts distinguish several stages of development of esophageal varicose veins, each with its own developmental characteristics, different from the list of manifestations, and require a certain therapeutic effect, which makes it possible to prevent further exacerbation of the pathology. Thanks to modern diagnostic methods, it is possible to determine the presence, stage and stage of development of the disease.
The extent of the extent of the veins in the stomach and varicose veins is as follows:
- the first degree at which there is a slight change in the lumen of the veins in the body. Varicose veins characteristic of grade 1 esophagus are not noticed by the patient, as they rarely have definite and pronounced symptoms. The esophageal veins have an average lumen of 5 mm, which is not much different from their healthy condition. However, they are even less flexible than this size, as small changes in their lumen lead to a decrease in blood flow intensity and the overall quality of blood circulation in the affected organ is disrupted. Routine examination of this organ reveals grade I varicose veins;
- the second degree is characterized by an increase in the lumen of the veins up to 10 mm in the diseased organ, the rate of blood flow through the veins gradually decreases, which negatively affects the condition of the veins: they continue to lose their elasticity, the walls gradually thin, which can cause bleeding due to rupture;
- in the third stage of exacerbation of the pathology, the lumen of the veins in the esophagus and stomach dilates by more than 10 mm, the blood vessels are close to each other due to their dilation, and may even cause mild bleeding. Often, in the third stage of the disease, severe bleeding occurs, which causes the patient to die and poses a real threat to the life of the patient with varicose tissue of the gastrointestinal tract. .
The above classification of esophageal varicose veins allows the existing lesions of the organ veins to be classified to some degree and treatment to be initiated, which has a positive effect on the patient's condition. Treatment of esophageal varicose veins should be selected by a physician who selects the exposure regimen and exposure variant based on the study and analysis of the patient's general condition, taking into account the specifics of their body.
The stomach returns
The extent of the veins, due to the negative change in their condition, can also be observed in the stomach. In this case, as in the case of esophageal varicose veins, the elasticity of the vein wall gradually decreases, and the likelihood of bleeding is significant. Modern diagnostic methods allow the timely detection and treatment of the pathology in question.
Methods for treating varicose veins localized in gastric tissues differ, but each aims to eliminate the cause of this condition. The National Chemical Center of the Russian Academy of Medicine provides the following data on the causes and methods of treatment of esophageal and gastric varicose veins:
- the manifestations of varicose veins in the esophagus and stomach are treated according to the method described in the book of leading experts in gastroenterology, a distinction is made between identified diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and this technique and a detailed description of the manifestations of such diseases. rare lesions such as pathologies of the operated esophagus, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that are difficult to diagnose provide the greatest amount of information for the compilation of a regimen of therapeutic effects for both therapists and narrow gastroenterologists;
- Zdenek Marzhatka, one of the leading experts in gastroenterology and esophageal diseases, accompanied by damage to the veins in his tissues, describes in detail the various methods of diagnosing the disease, the types of tissue endoscopy. the stomach and esophagus.

Today, more and more modern diagnostic methods are being used to prevent the further exacerbation of existing pathology, with the aim of examining the condition of the tissues of the affected digestive organs in more detail.
Diagnosis of the disease
Methods and options for diagnosing varicose veins in the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus and stomach) include the following manipulations and diagnostic procedures:
- Fibroesophagoscopy, which allows the cause of bleeding to be identified. In addition, this method makes it possible to determine the mechanical causes of bleeding, the condition of the wall of the esophageal veins.
- X-ray of the esophageal walls, which is more informative when contrast is applied.
Both options for diagnosing the disease in question can detect the cause of the bleeding, determine the condition of the vein wall, and determine the likelihood of rupture of existing aneurysms. The use of both diagnostic options allows us to detect not only the pathology of the esophageal and gastric veins and vessels with the greatest possible accuracy, but also to obtain as much information as possible about the pathology.
Possible complications
Because varicose veins in the esophagus and stomach tissues are particularly dangerous due to the likelihood of bleeding, the potential complications of this pathology should be considered. Significant damage to the digestive system, exacerbation of cirrhosis of the liver are the most dangerous consequences of this pathology of the veins.
Treatment methods
In the case of damage to the esophageal and gastric veins, the therapeutic effect to eliminate the risk of bleeding should take into account the stage of the pathological process, the patient's general health and the sensitivity of the body to the ongoing therapeutic effect. Modern medicine is constantly developing methods to affect the esophageal veins, which allows the most obvious manifestations of the pathology in question to be eliminated quickly.
Today, an integrated approach is used to treat the pathology of the esophagus and gastric veins, which consists of a traditional method of surgical and medical exposure. Each method has its own characteristics, can be used for certain indications and is prescribed by a doctor. The course of treatment should be monitored at all stages by the treating physician, who will make the necessary adjustments in a timely manner if necessary to prevent the likely risk of complications.
Traditional method
Above all, with traditional treatment for esophageal varices, the bleeding stops, which can be fatal. This also allows the implementation of additional therapeutic methods that ensure faster regeneration of damaged tissues and create the necessary scar at the site of esophageal vein damage.
To compensate for hypovolaemia and to prevent bleeding shock, a significant dose of vitamin K (calculated by your doctor) is injected into the patient's body, as well as a frozen plasma infusion (1-2 doses, intravenous transfusion). fulfilled).
Conservative method
In the event of severe bleeding, which is a real threat to the patient's life, a rubber inflatable probe can be used to ensure that the bleeding is stopped quickly. A probe is used to press the bleeding vessel, which stops the blood from moving. For example, the probe of such a device, the Sengstaken-Blackmore probe, is popular in eliminating bleeding during the formation of digestive organs, especially esophageal varicose veins. Crimped versions of such probes are also used and are widely used to treat bleeding and bleeding gastric ulcers in esophageal varices.
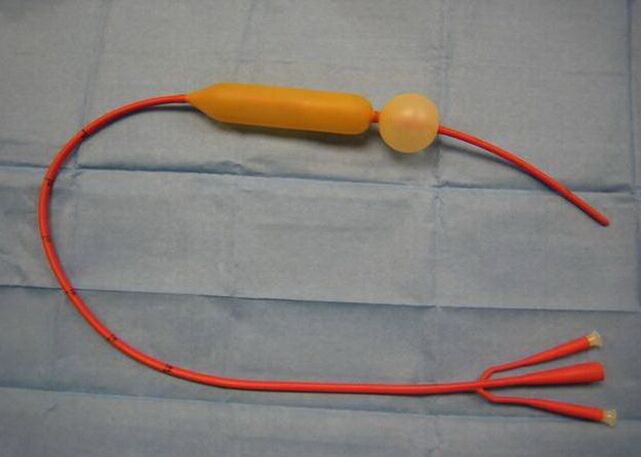
When the probe is placed under the site of a venous fracture, the esophagus can be washed with hot water at 40 ° C - a measure that often stops active bleeding and stabilizes the patient. However, in case of recurrent bleeding and their high intensity, intravenous and intramuscular administration of substances that also contribute to blood arrest is recommended in parallel with the use of probes. 10-20 ml of calcium chloride is injected intravenously. Do not use medications that increase blood pressure.
Endoscopic treatment
Because this disease of the esophageal veins is most often diagnosed on endoscopic examination, endoscopic hemostasis may be prescribed to eliminate the most common manifestations of the lesion (cessation of bleeding). This method involves suturing the affected areas of the esophageal veins, and this variant of the therapeutic effect is more advantageous than injectable sclerotherapy due to the more pronounced positive dynamics of the treatment.
Endoscopic treatment is characterized by the rapid cessation of bleeding and the prevention of the likely recurrence of the disease. The drug used in the endoscopic treatment of bleeding in the varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach is administered intravenously in an amount of 50 mcg, its effect is to increase visceral vascular resistance, which makes it possible to stabilize the patient's condition and prevent overactive blood loss. . This drug is preferred over other drugs that can be used to stop venous bleeding from the esophagus because it has fewer side effects, even with long-term use.
The use of an endoscope involves a special endoscopic examination of the esophagus, which is most often prescribed for bleeding for which the cause is not clear. This technique is very popular due to the high efficiency of this diagnostic method and the good positive dynamics of endoscope treatment (ligation). Endoscopic examination of the esophageal and gastric veins showed well at any stage of the development of the pathological process; In addition, this method makes it possible to detect the initial onset of gastrointestinal disease in connection with venous circulation and to identify esophageal varicose veins.
Using a balloon tamponade
The endoscopic exposure method also includes the use of such a variant of stopping bleeding from the esophageal veins, such as a balloon tamponade. This consists of touching special plugs at the site of vein damage. However, in case of heavy bleeding, the balloon tamponade may not be very effective, additional drugs should be used in the tissues of the vein wall to stimulate regeneration processes.
The classification proposed today is for the division of the varicose veins of the esophagus and makes it possible to determine the most effective system of therapeutic effects. Taking into account the specifics of the current stage of the pathological process, the body's perception of the drugs used and monitoring of ongoing treatment allows the treating physician to adjust in time and achieve the best results in stopping the bleeding and stabilizing the bleeding. the patient's condition.
Surgical intervention
Heavy bleeding that endangers the patient's life due to significant blood loss may require surgery.
Surgery may be prescribed for high blood loss when intravenous administration of plasma, blood and blood substitutes does not produce a positive result. There are several types of surgery for significant blood loss. Each is prescribed according to the indications prescribed by your doctor.
Today, the following types of surgery are recognized as the most effective:
- attaching a bandage made of special medical rubber. Such ligation of damaged veins allows for rapid cessation of blood circulation, cessation of blood loss, which can cause significant deterioration of the patient's condition;
- surgery, such as bypass surgery, leads to a decrease in blood pressure in the veins and, as a result, to the bleeding being stopped. During bypass surgery, an effect on the liver tissue is performed, with a special stent inserted in the middle of this organ, which creates a kind of bridge between the liver tissue and the esophageal tissue, which lowers blood pressure. Liver and portal veins with such a "bridge" receive reduced pressure, leading to cessation of bleeding;
- Splenorenal bypass surgery is a type of bypass surgery that helps prevent bleeding when varicose veins are detected in the tissues of the esophagus and stomach.
The listed surgical options may eliminate the increased blood pressure in the veins of the esophagus damaged by the varicose veins. Each is controlled by X-rays and provides the greatest positive effect during manipulations to stop bleeding.
Medical treatment of varicose veins
There is also a variant of the drug effect on the body to treat the initial stage of esophageal varicose veins. The choice of type of medication is determined by the doctor after examining the patient's body, determining the stage of the current pathological process. Indicators such as the sensitivity of the patient's body to the drug used and the likelihood of developing allergic reactions should be considered during this type of therapy.
The most common drugs used to treat the disease are those that have a pronounced effect on the veins:
The drugs listed have a number of possible side effects that should be considered when prescribing them.
Treatment with folk remedies
The reliability of drugs and traditional medicine methods has been tested for centuries, but its effectiveness is not high enough to cope with the manifestations of esophageal varicoseosis on its own. Conventional medicine can be used as a maintenance drug to increase the rate of recovery processes in the tissues of veins. For example, in the high probability of bleeding, it is recommended to take infusions and infusions of herbs that have an anti-haemorrhagic effect. Can be a collection of nettles, thyme, highland birds.
Treatment with folk remedies is also possible at home, which is especially important in the maintenance therapy of the disease, in the remission phase. As the esophageal varicose veins are a severe lesion that poses a serious risk to the patient’s health and life, the extent of the effect of the chosen conventional medicine should be considered. Home treatment is performed under the supervision of a permanent doctor.
Do you need a diet
In the diagnosis of gastrointestinal varicose veins, the issue of dietary choice should be considered one of the most important, as both the well-being and the indicators of continuous therapeutic effect depend on the food entering the patient's body. . The diet recommended for esophageal varicose veins involves adhering to a number of workable rules, which include the exclusion of certain foods and the inclusion of certain products that heal the whole body and especially the esophagus in the daily menu.

The diet of varicose veins in the esophagus should exclude the following foods and substances from the patient's diet:
- spices;
- large amounts of table salt;
- excessive amounts of oil, especially of animal origin;
- fried, canned, smoked foods that irritate esophageal tissues and can cause bleeding.
For varicose veins, as well as for cirrhosis, the diet should contain more cooked, steamed food, fermented dairy products perfectly support the necessary microflora in the gut without overburdening the digestive system. whole. Fragmented nutrition in small doses, regulation of the number of calories to prevent excessive effects on the digestive system prevents the exacerbation of existing pathology and maintains esophageal health.
Disease prevention methods
As a measure to prevent varicose veins, bad habits, including smoking, the consumption of alcoholic beverages, and fast food fast food must be ruled out.
Regular examination by a gastroenterologist will help identify venous disease in the early stages of pathology and begin treatment.
Healthy lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle should be made mandatory for those who seek to maintain a healthy digestive system.
Important components of success are the prevention of venous diseases, the use of vitamin preparations to maintain high immunity, and medical tests.
Exercise
Perform the necessary minimum physical exercises regularly to maintain the tone of your veins and to maintain the proper functioning of your digestive system.
Walking, light jogging, gymnastic exercises can be considered as good preventive measures in the development of varicose veins.























